DNS Records correlated to spamfiltering
Some of the DNS records are correlated to the mailing and it will affect the spam filtering activity too. In this article, I am discussing some of the DNS records correlated to spamfiltering. SPF, rDNS, DKIM and DMARC are the important dns records which are affecting spam filtering. Without proper setting of these records may cause detecting your mail as spam. For the smooth delivery of the mails, these dns records should be configured correctly.
How email works ?
Whenever we send some data over e-mail, the e-mail client interacts with the SMTP server to handle the sending. The SMTP server on the host may have conversations with other SMTP servers to deliver the e-mail. Starting from the very first level of mail communication, I will explain how email service is related to DNS service with the help of a flow chart.
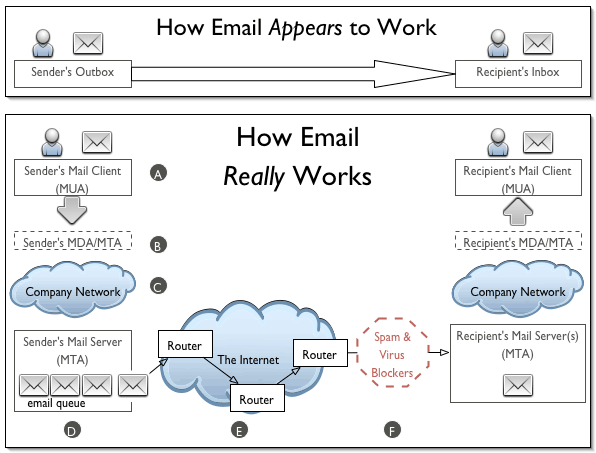
MX Records
In the first stage of the mail delivery process an email address matched to a domain name, and the DNS converts the domain to IP address and send the data. So the first DNS record checking in the mail delivery process is the A record for the domain. Then the mail server will check for the mail server for the destination domain, so it look for the MX of the domain. Also the MX of the domain should have an A record set to an IP address of the mail server.
MX record for the domain.com
domain.com MX 0 mail.domain.com
mail.domain.com A 123.321.123.321
These are the minimum DNS records needed for the mail server working. Now we need to add few DNS records correlated to spamfiltering which will help to smooth delivery of the mails without filtered it as spam mails in spam filtering solutions used in the destination mail servers.
PTR Records
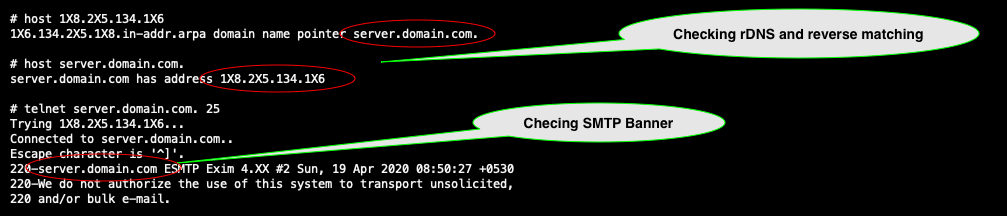
PTR records are used in reverse DNS lookups which are conducted by mail servers to make sure that the other mail server they are dealing with is who they say they are. Basically, this record tells other mail servers that the IP of our mail server is authoritative for sending and receiving mail for our domain. In normal case we set the hostname as the rDNS for the IP. When a mail server receives a request from your domain’s mail servers, it will take the IP provided (of your mail server) and do a reverse DNS lookup and confirm the reverse DNS matching the SMTP Banner of the mail server. Also confirms the reverse DNS and A record for the domain are matching, if A record and reverse dns are not matched, the smtp test will show “Reverse DNS Mismatch”
Unsolicited mails or Spam mails
Spam is electronic junk mail or junk newsgroup postings. Some people define spam even more generally as any unsolicited email. However, if a long-lost brother finds your email address and sends you a message, this could hardly be called spam, even though it is unsolicited. Real spam is generally email advertising for some product sent to a mailing list or newsgroup.
Spoofing
Spoofing is the act of disguising a communication from an unknown source as being from a known, trusted source. It can apply to emails, phone calls, and websites, or can be more technical, such as a computer spoofing an IP address, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), or Domain Name System (DNS) server.
Spoofing used to gain access to a target’s personal information, spread malware through infected links or attachments, bypass network access controls, or redistribute traffic to conduct a denial-of-service attack. It is often the way a bad actor gains access in order to execute a larger cyber attack such as an advanced persistent threat or a man-in-the-middle attack.
Prevent mail spamming
Now we are going to create a special kind of record, it will tell the other mail servers about the authorised mail server of your domain. This record will tell those servers to only trust mail coming from IP addresses and hostnames that you specify. We will need to create an SPF record that contains our domain and the IP address of our mail server.
SPF record added to the DNS zone for the domain and it is a specially-formatted version of a standard DNS TXT record. An SPF record looks something like this:
Example: google.com. 3599 IN TXT “v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com ~all”
You can generate SPF using Online SPF Generator
DKIM Record
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is a method to validate the authenticity of email messages. Each email sent from the mail server signed with a private key and validated at the remote server using the public key. This will help to verify the mails are unaltered in the trust process.
Similar to SPF, DKIM also uses DNS TXT records with a special format. When a private/public key pair is created, the public key is added to your domain’s DNS:
Example: pm._domainkey.domain.com IN TXT “k=rsa\; p=XXXXXXXX”
DMARC Record
Determination of a fraudulent email is based on a combination of a SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and/or DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) check. Once the recipient email server determines the status of the email, it then looks at the DMARC DNS record to understand how it should react.
Example: v=DMARC1;p=reject;pct=100;rua=mailto:postmaster@dmarcdomain.com
In this sample, the DMARC record instructs the recipient email server to reject or delete any email it suspects as being fraudulent and to send an aggregated report back to a specified email address as evidence.
Conclusion
Hope you understand the DNS records correlated to spamfiltering. Proper configuration of these DNS records helps the smooth delivery of mails to the inbox of the destination mail account. Most of the case, the mails delivered to spam box is due to the poorly configuration of these dns records. Lots of online tools are available to check these DNS records, you can use any of them to verify these records. And surely you can contact our admins for fixing these DNS records for your mail server.
